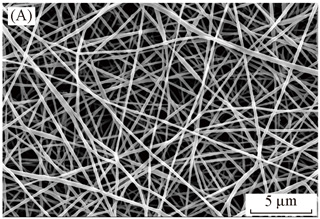
Although tobacco tow occupies the absolute market share of acetate fiber (CA), its market in high-grade apparel fabrics, linings, technical textiles and other fields has opened up. Among them, cellulose acetate membrane materials have been widely used in the field of filtration and separation in the field of technical textiles, and have also achieved great market potential for the development of high-end products. Here are some of the latest developments. Hollow fiber membrane Membrane separation and filtration are the most effective separation and concentration methods and have been successfully used for the filtration of nanoparticles. By changing the preparation conditions of the film, different porosity film materials can be obtained. Cellulose acetate has been widely used for reverse osmosis (RO), microfiltration (MF) and gas separation operations. It is an environmentally friendly raw material for membrane material preparation. It is non-toxic and relatively inexpensive. It has been successfully used in brackish water, sea water desalination, ethanol, methanol filtration and urea total penetration treatment. For example, the cellulose acetate nanofiltration membrane bioreactor (NF-MBR) used for wastewater treatment is a U-shaped hollow fiber membrane, the number of single filaments is 85,000, and the specific surface area of ​​a single module is 11.7 m2. Japan Daicel Corporation FT50 type CA ultrafiltration membrane (UF) has been widely used in the removal of turbidity of groundwater and industrial water, green cellulose acetate hollow fiber ultrafiltration membrane developed by France Chemique Lab for wastewater treatment, biological actives Separation and gas separation. The UF membrane is prepared by using natural or biodegradable raw materials. The solvent used in the membrane preparation process is methyl lactate or ethyl lactate which is a green solvent system, and its acute LD50 is 5 g/kg. Among the medical membrane materials, Toyobo's cellulose acetate membranes have been used in artificial kidneys, and modified cellulose triacetate (CTA) membranes have also been used clinically in hemodialyzers. 2 Bio-based fibers Researchers at the North American Center for Agricultural Applied Research used agricultural waste, such as corn fiber, rice hulls, and wheat straw, as raw materials for the preparation of cellulose acetate. Corn fiber-based biomass raw materials for the preparation of cellulose acetate need to be pre-treated, usually corn fiber material at 55 °C, forced air drying conditions for 4 h, after crushing, control a certain degree of granularity stored at room temperature. Before the pretreatment, hexane was used to remove the traces of the material. The mass fraction of the material was controlled at 15%, rice shell 15%, and wheat straw material 8.5%. The pretreatment was completed in a reactor and the temperature was 121 °C for 4 h. The pretreated material enters the acetylation process. The acetylation conversion in the current test is about 25%. In an exploratory study of the production of cellulose acetate using renewable biomass resources, the researchers used unrefined biomass feedstocks, such as palm kernel powdered materials, dissolved in ionic liquid (BMIMCI) at 45 °C, and lignocellulose. Selective separation, modified cellulose can be used as vinegar raw materials. The acetification reaction is carried out at 55 °C and the process is very compact. CTA has a degree of esterification of 2.9 and can be used for fiber or film processing. The study also showed that the choice of biomass raw materials is diversified, and the available biomass includes bagasse, tulip tree, hybrid poplar, oak, Japanese pine, and rice shells. France's Roquette uses plant starch to synthesize bio-based cellulose acetate, which provides eco-friendly raw materials for Rhodia's cigarette acetate tow. It also has advantages in terms of cost. The study is currently in progress. 3 nanofibers The preparation of nanofibers can be traced back to the 1930s, and the first polymer nanofibers to be successfully spun is cellulose acetate. In recent years, advances have been made in the technology and application of submicron-nanocetate fibers. For example, the Polish Institute of Fiber and Medicinal Plants used the electrospinning method to successfully obtain modified cellulose acetate nanofiber webs. The monofilament diameter was controlled between 200 and 600 nm, and it had antibacterial function and very high particle capture efficiency. The cellulose acetate spinning solution configured with the acetone/DMAc/ethanol complex solvent system (composition ratio 4/1/1) was prepared by electrospinning to obtain a nanofiber web with a monofilament diameter ranging from 100 to 500 nm. The test results prove that the nanofiber web has a controlled release of liquid medicine. Donghua University used a mixture of cellulose acetate and silk protein and electrospinning to obtain a nanofiber web with a diameter of 50 to 300 nm. This shows good mechanical properties, tear strength of 88.9 cN/mm2, and elongation at break of 12.77. %. The cellulose acetate nanofiber membrane developed by the researchers showed good separation performance as a particle separation medium. The fiber was prepared using methylene chloride, formic acid, and trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) as a solvent, and 8% of the spinning solution was placed at room temperature. The degree of esterification of the cellulose acetate used was 2.5. Using electrospinning method, voltage 15 kV, and the collection device spacing 10 cm. The monofilament diameter of nanofiber membranes ranges from 100 to 300 nm. The quality of membrane material is monofilament diameter (0.19±0.05) μm, thickness 406 μm, porosity 87%. Interlock Jersey Fabric Polyester,Cool Max Interlock Knit Fabric,Pure Color Interlock Knit Fabric,Interlock Fabric Textile Shaoxing Winfar Knitting & Embroidery Co.,Ltd. , https://www.wfknitting.com
For more content, please follow this site